Overweight or Obese? – Calculate Your Risk
More than 6 out of 10 American adults are overweight or obese and that figure is rising. Being overweight or obese can cause many serious health problems.
Health professionals often use BMI and waist circumference together to assess whether someone is overweight or obese and to assess their risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
What is body mass index (BMI)?
BMI is calculated by dividing weight by the square of height as follows:
BMI = Weight (kg)/Height (m)2
To find your weight classification (if you are an adult), see which of these BMI ranges your weight falls into:
- Under 18.5 Underweight
- 18.5–24.9 Healthy weight range
- 25.0–29.9 Overweight
- 30.0–34.9 Obesity I
- 35.0–39.9 Obesity II
- 40.0 (and above) Obesity III
Limitations of BMI
BMI is less accurate for assessing healthy weight in some groups of people because it does not distinguish between the proportion of weight due to fat or muscle.
Why measure waist circumference?
Carrying excess body fat around your middle is more of a health risk than if weight is on your hips and thighs. Waist circumference is a better estimate of visceral fat, the dangerous internal fat that coats the organs.
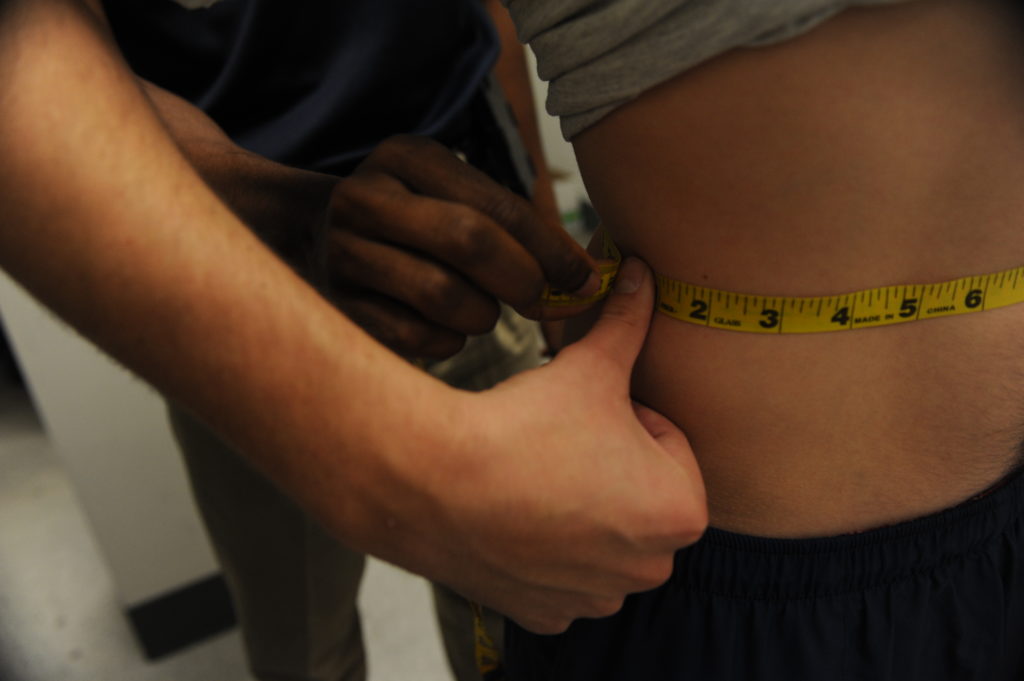
How do I measure my waist circumference?
To find out your level of risk, it is important to measure your waist circumference accurately. The correct place to measure your waist is roughly in line with your belly button.
Waist circumference and disease risk
These are the waist circumference thresholds that indicate an increased risk of disease:
If you are a woman:
- your risk is increased at 80 cm or more
- your risk is high at 88 cm or more
If you are a man:
- your risk is increased at 94 cm or more
- your risk is high at 102 cm or more
Limitations of waist circumference
Waist circumference is less accurate in some situations, including pregnancy; where the person has a medical condition involving enlargement of the abdomen; for certain ethnic groups; and for children and young people.
What are the health risks of being overweight or obese?
Being overweight or obese can directly contribute to a person developing many serious health problems, including:
- type 2 diabetes
- high blood pressure
- cardiovascular disease
- sleep apnea
- and osteoarthritis.
Many of these diseases can be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight and following a healthy lifestyle, including a well-balanced diet and regular physical activity.
How can I lose weight?
Probably the most successful way to promote weight loss is to have a lifestyle that combines improved nutrition and increased physical activity. Your goals should focus on behavior change and improved health, rather than weight loss.
Some people may need a more intensive approach, such as a very low energy diet, weight loss medication or bariatric surgery. This is especially likely in those who are obese, have other risk factors, or who have been unsuccessful in reducing weight by changing their lifestyle.
